Abstract
The paper reviews a threat hunters methodology and aims to help organizations protect themselves against advanced persistent threats(APT). The paper starts off by explaining the first hacking case and explains how attacks have advanced over the years. The rest of the paper talks about the threat hunters methodology and how it can be used to combat APT groups.
Introduction
Hackers have been infiltrating and pilligings networks for decades now. In 1903 the hacker Nevil Maskelyne was caught sending disrespectful messages in morse code through the auditorium's projector. Hackers have always been around but responding to and protecting ourselves from these malicious actors is relatively new. Threat hunting focuses on finding these malicious actors commonly referred to as advanced persistent threats(APT).
Hackers have advanced tremendously over the years. The days are over where you only have to worry about teenagers in their mom's basement. In today's world we have nation states, sophisticated criminal organizations, and large financially motivated groups of individuals coming after your organization. Advanced persistent threats(APT) are the new modern day hackers. They are sophisticated, well funded, organized, and motivated.
The rise of APTs gave birth to the term threat hunting. Threat hunting is defined as “the process of proactively and iteratively searching through networks to detect and isolate advanced threats that evade existing security solutions”. The job of a threat hunter is to find sneaky APT that have infiltrated your network. Since hackers have upped their sophistication and organization threat hunters will have to as well. Threat hunters need a methodology to hunting down these APT groups. Luckily there are whole frameworks with millions of dollars of research put into them to help solve this very problem.
Discussion
Methodology
The Sqrrl Security Analytics Company created a simple framework for threat hunting. This framework should be ran in a loop meaning once you reach the last step in the framework you go back to the beginning. The framework states that the threat hunting loop consists of creating a hypothesis, investigating via tools, discover new techniques, and Inform and enrich analytics.
Hypothesis
|
|
Investigating via Tools
|
|
Discover new Tools, Tactics, and Techniques(TTP)
|
|
Inform and enrich analytics
|
|
Creating a Hypothesis
A scientific hypothesis is the initial building block in the scientific method. Many describe it as an "educated guess," based on prior knowledge and observation. There are two key components to creating a hypothesis for threat hunting. The first component like the definition states is an observation. An example of an observation might be that the hunter sees something fishy in the logs that looks suspicious. Another observation might be that the hunter heard about a particular APT group that is currently active. The second component is that the hypothesis must be testable. For example you must be able to narrow down on a piece of data that could be burriod in gigabytes of logs.
Investigating via Tools
Once the hunter has formed a hypothesis he can begin to test via tools and techniques. These tools and techniques can be broken down into three main categories:
- Log Analysis
- Network Analysis
- Host Analysis
Log Analysis
Log analysis can be done at both the network and host level. For example at the network layer you might have an IDS or IPS that will store logs. At the host layer you will generally have a plethora of event logs to search through, at least on a windows machine.
The logs at the network and host layer need to be sent to a central location for storage and analyzation. Having these logs in a central database will make quirering easier and it will make it more difficult for hackers to cover their tracks by deleting logs of a compromised machine.
Network Analysis
Encryption, storage, and processing limitations can impact network analysis greatly. Threat Hunters should focus their analysis on examining four key network characteristics:
- Number of outbound network connections
- Duration of connections
- Amount of data exchanged
- Frequency of connections
Hunters can take advantage of network flow analysis, protocol analysis, and statistical analysis. So by using these four characteristics hunters can try to find anomalies in host on the network based on the way the host communicates.
Host Analysis
On windows everything you do will most likely have some sort of event log associated with it. Hunters should pay attention to these host based logs. Hunters should also pay close attention to:
- Running Processes
- Running Services
- Auto Start Locations
- Antivirus alerts
- Host based IDS/IPS logs
- Privileged Users
- Privileged Groups
Like in the network analysis phase we are looking for anomalies in host.
Tools, Tactics, Procedures(TTP)
Searching for malware hashes, IPs, and other artifacts will not be enough to stop your average APT group. You will need to discover new tools, tactics, and techniques that these advisories are using.
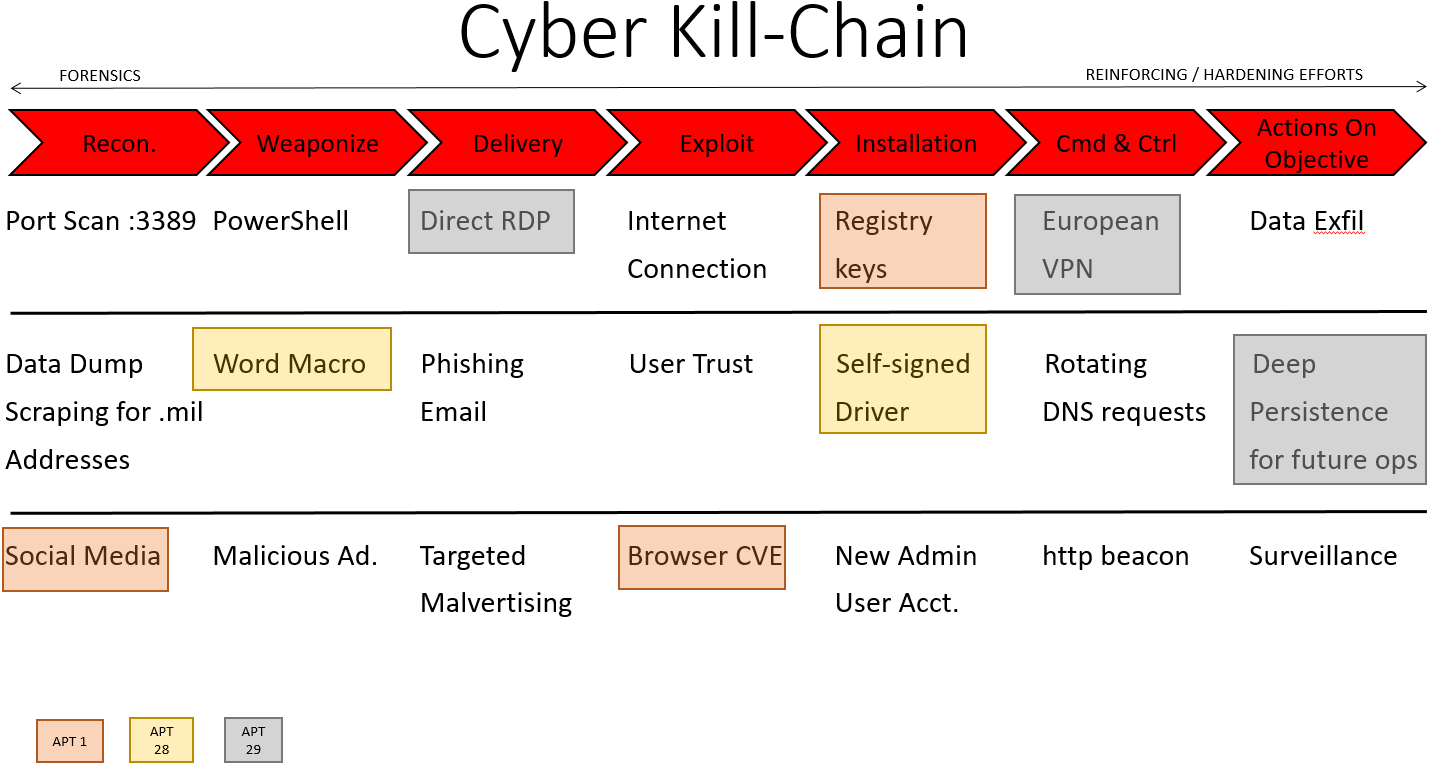
Cyber KillChain
The cyber kill-chain was developed by Lockheed Martin and it is a way for hunters to help prevent attacks. It allows the defenders to discover tools tactics and techniques used by APT groups.
Instead of focusing on finding artifacts the hunter should instead spend his time focusing on certain techniques that the APT group uses such as pass the hash. The hunter can focus on a particular part in an attackers methodology. The hunter can focus on these phases:
- Recon
- Weaponize
- Delivery
- Exploit
- Installation
- Command & control
- Objective
There are weakness and bottlenecks in each phase of the methodology. For example in the command and control phase an attacker must beacon home somehow. This can involve a piece of malware sending http request to the command and control server. A hunter can take advantage of this bottle neck and specifically look for this type of behavior. Learning how these APT groups operate can help defenders discover zero day malware and other techniques.
Inform and enrich analytics
Once you have mapped out an APTs tools, tactics, and techniques you can use these findings to find other compromised host. You can also automate the task of discovering these indicators of compromise which will make your job easier and it will allow you to quickly detect a certain methodology.
Conclusion
In today's world we can't just rely on the traditional blue team practices. Antiviruses, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems are not enough to beat someone who is organized, intelligent, and persistent. Organizations should assume that they are already breached and that hackers have infiltrated their network. Advanced persistent threats are out their in the form of nation states, criminal organization, and other highly motivated groups. Hunters need to have a methodology to detect these unknown attacks and groups. We have never been so connected and this makes everyone is a potential target.
Comments
Post a Comment